Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maeyama, Shinya*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Asahi, Yuichi; Ishizawa, Akihiro*
Nature Communications (Internet), 13, p.3166_1 - 3166_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:93.82(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Turbulent transport is a key physics process for confining magnetic fusion plasma. Recent theoretical and experimental studies of existing fusion experimental devices revealed the existence of cross-scale interactions between small (electron)-scale and large (ion)-scale turbulence. Since conventional turbulent transport modelling lacks cross-scale interactions, it should be clarified whether cross-scale interactions are needed to be considered in future experiments on burning plasma, whose high electron temperature is sustained with fusion-born alpha particle heating. Here, we present supercomputer simulations showing that electron scale turbulence in high electron temperature plasma can affect the turbulent transport of not only electrons but also fuels and ash. Electron-scale turbulence disturbs the trajectories of resonant electrons responsible for ion-scale micro-instability and suppresses large-scale turbulent fluctuations. Simultaneously, ion-scale turbulent eddies also suppress electron-scale turbulence. These results indicate a mutually exclusive nature of turbulence with disparate scales. We demonstrate the possibility of reduced heat flux via cross-scale interactions.
Okamoto, Masao*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 77(6), p.536 - 546, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Ara, Katsuyuki
Heisei-8-Nen Denki Gakkai Zenkoku Taikai Koen Rombunshu, 0, p.S8.33 - S8.36, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Keishi; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Kasugai, Atsushi; Takahashi, Koji; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Hirata, Yosuke*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 71(10), p.1029 - 1037, 1995/10
no abstracts in English
Tsuneoka, Masaki; Fujita, Hideo*; Imai, Tsuyoshi; *; *
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, D, 115(5), p.539 - 544, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
M.Hoek*; Nishitani, Takeo; Ikeda, Yujiro; Morioka, Atsuhiko
JAERI-M 94-002, 25 Pages, 1994/01
no abstracts in English
Tsuneoka, Masaki; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*
Denki Gakkai Rombunshi, B, 114(11), p.1179 - 1180, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Nakata, Motoki; Honda, Mitsuru; Yoshida, Maiko; Urano, Hajime; Maeyama, Shinya; Nunami, Masanori*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
no journal, ,
First-principle based gyrokinetic simulation is a powerful method for investigating turbulent transport in magnetically confined fusion plasmas, and the quantitative evaluations of the prediction capability through comparisons with existing experiments and the model improvement are important issues. In this study, a local gyrokinetic turbulence code GKV-J is extended to incorporate realistic tokamak equilibria to realize the first principle based turbulent transport simulations on JT-60U tokamak. In addition to clarifications of the micro-stability properties depending on the radial locations, the turbulence simulation results successfully reproduce the experimental results on ion and electron heat diffusivity in the core region, where the conventional fluid-type reduced transport model shows some deviations. Also, the impact of shaping on turbulent transport properties is identified for JT-60SA tokamak.
Nakata, Motoki; Honda, Mitsuru; Yoshida, Maiko; Urano, Hajime; Maeyama, Shinya; Nunami, Masanori*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
no journal, ,
First-principle based gyrokinetic simulation is a promising approach for investigating turbulent transport in future burning plasmas such as ITER an DEMO. In this study, ITG-TEM driven turbulent transport simulations on the realistic JT-60U tokamak equilibrium are realized by using a local gyrokinetic turbulence code GKV-J. Linear micro-stability analyses on several radial locations revealed that ITG, ITG-TEM, and TEM modes are dominant for inner, middle, and outer core regions, respectively. The nonlinear turbulence simulation results successfully reproduce the experimental results on ion and electron heat diffusivity in the core region, where the conventional fluid-type reduced transport model shows some deviations. Also, different nonlinear dependences of the turbulence/zonal-flow energy on the ion/electron heat and particle transport levels are newly identified, i.e., weaker impact on the electron heat and particle transport compared to the ion heat one.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
One of the key issues for producing high current beams in JT-60SA is a uniform production of the negative ions over the large ion extraction area. Non-uniformity of the negative ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source was improved by modifying the magnetic filter in the source from the PG filter to a tent-shaped filter. In this work, in order to clarify the influence of the magnetic filter modification on arc efficiency and co-electron current is investigated by means of measurements of H ion, H atoms, co-electron current and beam intensity. As a result, the arc efficiency increase due to increase of H ions and H atoms by reduction of filter field. Although the higher electrons current was extracted than the original PG filter, the co-extracted electron could be suppressed by optimization of the bias voltage. This result contributes to extend the pulse duration time up to 100 s for JT-60SA.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Differences of confinement properties between hydrogen and deuterium plasmas are studied in numerical experiments of ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using a full-f gyrokinetic code. Through systematic heating power and plasma size scans, it is found that a Bohm like scaling of the confinement time 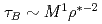 is given by stiff ion temperatur profiles, which are produced by intermittent bursts of avalanche like non-local transprt. Here,
is given by stiff ion temperatur profiles, which are produced by intermittent bursts of avalanche like non-local transprt. Here,  is the mass of ions and
is the mass of ions and 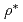 is the normalized Larmor radius. From this result, it is shown that the confinement time of the ion temperature gradient turbulence is proportional to the mass of ions.
is the normalized Larmor radius. From this result, it is shown that the confinement time of the ion temperature gradient turbulence is proportional to the mass of ions.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Maeyama, Shinya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Watanabe, Tomohiko*
no journal, ,
A novel parallel optimization technique for extreme scale CFD simulations is developed on the K-computer, and strong scaling of finite difference and spectral fusion plasma turbulence codes is improved toward million-core regimes. The optimization technique consists of a multi-dimensional and multi-layer domain decomposition, optimized process mapping on a three dimensional (3D) torus network, and overlap of computations and communications using communication threads. The improved strong scaling dramatically expanded capabilities of the fusion plasma turbulence codes both in problem sizes and time-scales, and enabled us to study critical issues in ITER such as the plasma size scaling of ion turbulent heat transport, and the electron heat transport induced by multi-scale electron turbulence.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
This lecture aims to overview progress in gyrokinetic simulations of turbulent fusion plasmas. Firstly, theoretical frameworks of physical models from the 6D Vlasov equation to the 5D gyrokinetic equation are presented, and then, simulation models to treat multi-scale physics in the 5D gyrokinetic equation are discussed. Secondly, properties of numerical approaches, namely, Lagrangian and Eulerian approaches are described, and a role of numerical dissipation in collisionless plasma turbulence simulations is discussed. Thirdly, recent advances in gyrokinetic simulations are reviewed focusing on multi-scale simulations such as numerical experiments using full-f gyrokinetic models and ion-electron multi-scale electron turbulence simulations.